![]()
![]()
 以抗凝血蛇毒蛋白研究細胞在玻片上的附著與移動
以抗凝血蛇毒蛋白研究細胞在玻片上的附著與移動
![]() 快速移動癌細胞的細胞骨架
(cytoskeleton) 之免疫螢光染色
快速移動癌細胞的細胞骨架
(cytoskeleton) 之免疫螢光染色
綠色影像是微小管 (microtubule) 之染色, 紅色影像是肌動蛋白 (actin) 之染色![]()
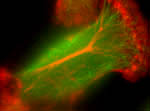 合成的影像
合成的影像
簡介
台灣地處亞熱帶地區,適合各種蛇類的生存,由於早期不少毒蛇咬人致死的例子,對蛇毒的研究從日據時杜聰明到後來的台大李鎮源、張傳炯、楊振忠等人努力經營成為台灣一個有相當歷史的研究領域(Chang and Lee 1963;Chang and Young 1969;楊 and 羅 1996)。根據Mao等人1984年和1986年的報告指出目前台灣已知的蛇類共有55種,其中無毒蛇36種,毒蛇19種。19種毒蛇中,包括海蛇7種、陸地蛇12種。常見的六種陸地毒蛇分別為屬於眼鏡蛇科(Family Elapidea)的雨傘節(Burgarus multicinctus)和中國眼鏡蛇(Naja naja atra)及屬於蝮蛇科(Family Viperidae)的:
鎖蛇(Vipera russelliformosensis)
百步蛇(Deinagkistrodon acutus)
龜殼花(Trimeresurus mucmsquamatus)
赤尾青竹絲(Trimeresurus gramireus)
(Mao et al.,1984;1986)
而本論文所探討的蛇毒蛋白rhodostomin 為馬來亞蝮蛇,其毒液成份rhodostomin與本土赤尾青竹絲(Trimeresurus gramireus)的trigramin相似(Huang et al.,1987 a;1987b)。它屬於蝮蛇科;馬來蝮蛇屬,分布在東南亞,包括越南、泰國、馬來西亞、印尼等地(Daltry et al.,1996)依據Daltry等人的報告指出,Calloselasma rhodostoma由於地域性的食物來源(例如爬虫類、兩生類等等)的不同導致蛇毒的成份有變異性(variation)(Daltry et al.,1996)。
蛇毒為複雜的混合物,包括了80%∼90%的水份,和各種多勝鏈,包括oligopeptidle、enzymes、glycoproteins等,及其它少量物質(Ghosh and Chaudhuri 1968;Russell 1983a;1983b;Kochva 1987),不過整體來,說蛇毒蛋白以功能來區分,可以分成神經性毒,血液性毒和肌肉性毒(myotoxin)(Russell 1983a;1983b)。而血液性毒中,又包含了各種可控制血液凝固的因子,包括促進血液凝集或是阻止血液凝集的各種蛋白,以影響血小板凝集的功能為例⊿在目前已知的出血性蛇毒中(Ouyang et al.,1983a;1983b;1983c;Huang et al.,1984;1987a1987b)有三種成份會抑制血小板凝集:(1)ADPase(Boffa et al.,1974;Ouyang et al.,1983b;1986)。(2)X-fibrinogtenase(Ouyang et al.,1985)。(3)RGD containing peptide為一種競爭性纖維蛋白原受體抵抗劑(Huang et al.,1987b;1989a)。而另外一種蛇毒蛋白會引起血小板的凝集和釋放反應(Davey et al.,1965;Kirby et al.,1979;Sch maier et al.,1980;Ouyang et al.,1980;1983d;Vargafting et al.,1980;Teng et al,1989)。而不論是神經性毒,還是血液性毒,其目的都是為了減少獵物抵抗(kini et al.,1990;Quyong et al.,1992)。
擁有RGD序列的一類毒蛇蛋白是在出血性毒中研究較為詳細清楚的蛋白家族之一,其成員為含約48-83個胺基酸的小蛋白分子,憑藉其高親合力競爭纖維蛋白原(fibrinogen)在血小板上的結合部位(integrnαⅡbβ3而抑制血小板凝集(Huang et al.,1987a,b;Huang et al.,1989; Glould et al.,1990)。這一類蛋白曾被台大藥理所學者,如歐陽兆和和黃德富廣泛的研究(Huang et al.,1987 ab;Huang et al.,1989)。此家族蛋白有些成員是在核酸序列未知的情況下,以蛋白生化學的方式定出其胺基酸順序(Huaug et al 1987)。並在1990年以其功能將這家族蛋白質取名為:disintegrin(Gould et al.,1990)。這是一個龐大的蛋白家族,被此之間有相當高的相似性(homology)(Gould et al.,1990),連哺乳類也有相類似的基因 (ADAM),和細胞之間辨識和發育有密切關係。 Disintegrin 廣泛的出現在各種蛇類的毒液中,例如台灣的龜殼花(Trimenesurus mucrosquamatus)和赤尾青竹絲(Trimeresurus gramireus)也分泌disintegrin類蛋白trigramin(Tsai et al.,1994.)此外,除了蛇類,水蛭(Macrobdella decora)也在唾液中有功能類似的蛋白(Mclane et al.,1995)。由於這類蛋白抑制血小板凝集的能力很強(Dennis et al.,1993;Chiang et al.,1994),曾被學者建議發展成為抗血栓疾病的藥物(Verstrate andZoldheyi,1995)。
這部分實驗主要以人工合成的 rodostomn 基因在大腸菌大量表現 rhodostomin 蛋白後,憑藉它與integrin 的高親合力,提供一個很好的模型來觀察細胞與disintegrin 蛋白的交互作用。尤其在論文後期發現以 GST-rhodosromin 處理的蓋玻片,不需要其它的激活劑即足以刺激血小板完全伸展(fully spreading)成為荷包蛋狀的形態;相教之下,同樣具有 RGD 序列的 fibrinogen 蛋白,為血小板凝集之natural ligand,卻無此功能,因此基因工程之rhodostomin 提供了一個研究細胞黏著及伸展時訊息傳導的新方向。
這部分實驗主要包括以下幾個部份
1. 選殖和表現人工合成之rhodostomin 基因
依據已知的rhodostomin 蛋白之氨基酸順序和大腸菌的codon usage,以人工合成的十一段相互配對的oligonucleotide 合成人工rhodostomin 基因,是繼disintegrin 類蛇毒echistatin(Gan et al.,1989)之後,第二個以人工方式合成的基因,首創在合成人工基因時以PCR 方式提高成功率,在接入表現質體後,可在大腸菌大量表現及純化。
2. 以GST-rhodostomin接合蛋白處理的介面研究細胞黏貼的特性。
以GST-rhodostomin 接合蛋白覆蓋蓋玻片,可發現有加速細胞黏貼的功能,將RGD motif突變為RGE的突變蛋白,即喪失加速細胞黏貼功能。另外以含 RGD peptide 和抗RGD peptide的抗體,具有降低GST-rhodostomin之功能,証明rhodostomin的功能區域在RGD位置,而且也是首創以disintegrin 蛇毒蛋白處理之介質來研究細胞黏貼的特性,而發現有類似胞外介質的特性。
3.証明GST-rhodostomin的抗凝血能力
以血小板凝集測定儀,發現大腸菌表現之GST-rhodostomin蛋白和天然rhodostomin蛋白(購自Sigma),有相等抑制血小板凝集的能力。
4. 發現immobilized GST-rhodostomin蛋白即足以誘發血小板的完全伸展和FAK的磷酸化。
這些作用是透過rhodostomin上的RGD motif聯結(cross link)血小板細胞膜上的integrin αⅡbβ3分子而造成。分別以GST-rhodostomin 蛋白處理的介面,會刺激血小板的完全伸展,而伸展與否和 FAK 的磷酸化有直接的相關。以peptide(GRGDSP)和抗體(抗integrin 抗體)作競爭實驗知道,GST-rhodostomin 作用是透過rhodostomin 上RGD motif和血小板上integrinαⅡbβ3分子作用而引發。以抗integrinαⅡbβ3的抗體處理的介面,一樣也有誘導血小板伸展的功能,顯示這些作用是透過聯結(cross link)血小板上integrinαⅡbβ3分子而達成。
5.血小板的完全伸展與鈣離子的通透,PKC的活化和actin聚合有密切的關連。
以抑制劑來研究血小板在 GST-rhodostomin 介質上的伸展,發現胞內和胞外的鈣離子都參與伸展的作用,而且PKC 的活化和actin 的聚合都絕對需要,缺一不可。
![]() *
重點閱讀
*
重點閱讀
1. Chang, H. H., Hu, S. T., Huang, T. F., Chen, S. H., Lee, Y. H. & Lo, S. J. (1993). Rhodostomin, an RGD-containing peptide expressed from a synthetic gene in Escherichia coli, facilitates the attachment of human hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 190, 242-249. (Article from our research team)
2. Chang, H. H., Tsai, W. J. & Lo, S. J. (1997). Glutathione S-transferase-rhodostomin fusion protein inhibits platelet aggregation and induces platelet shape change. Toxicon 35, 195-204. (Article from our research team)
3. Chang, H. H., Chang, C. P., Chang, J. C., Dung, S. Z. & Lo, S. J. (1997). Application of Recombinant Rhodostomin in Studying Cell Adhesion. J Biomed Sci 4, 235-243. (Review article from our research team)
4. Chang, H. H. & Lo, S. J. (1998). Full-spreading platelets induced by the recombinant rhodostomin are via binding to integrins and correlated with FAK phosphorylation. Toxicon 36, 1087-1099. (Article from our research team)
5. Chang, H. H., Lin, C. H. & Lo, S. J. (1999). Recombinant rhodostomin substrates induce transformation and active calcium oscillation in human platelets. Exp Cell Res 250, 387-400. (Article from our research team)
6. Chang, H. H., Shih, K. N. & Lo, S. J. (2000). Receptor-mediated endocytosis as a selection force to enrich bacteria expressing rhodostomin on their surface. J Biomed Sci 7, 42-50. (Article from our research team)
7. Chang, C. P., Chang, J. C., Chang, H. H., Tsai, W. J. & Lo, S. J. (2001). Positional importance of Pro53 adjacent to the Arg49-Gly50-Asp51 sequence of rhodostomin in binding to integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Biochem J 357, 57-64. (Article from our research team)
8. Chang, H. H., Kau, J. H., Lo, S. J. & Sun, D. S. (2003). Cell-adhesion and morphological changes are not sufficient to support anchorage-dependent cell growth via non-integrin-mediated attachment. Cell Biol Int 27, 123-133. (Article from our research team)
9. Chang, J. C., Chang, H. H., Lin, C. T. & Lo, S. J. (2005). The integrin alpha6beta1 modulation of PI3K and Cdc42 activities induces dynamic filopodium formation in human platelets. J Biomed Sci 12, 881-898. (Article from our research team)
10. Lo, S. J. & Chang, H. H. (2005). Recombinant snake disintegrins used for mammalian integrin study. Toxin Reviews 24, 95-111. (Review article from our research team)
11. Sun, D. S., Lo, S. J., Lin, C. H., Yu, M. S., Huang, C. Y., Chen, Y. F., et al. (2005). Calcium oscillation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase positively regulate integrin alpha(IIb)beta3-mediated outside-in signaling. J Biomed Sci 12, 321-333. (Article from our research team)
12. Sun, D. S., Lo, S. J., Tsai, W. J., Lin, C. H., Yu, M. S., Chen, Y. F., et al. (2005). PI3-kinase is essential for ADP-stimulated integrin alpha(IIb)beta3-mediated platelet calcium oscillation, implications for P2Y receptor pathways in integrin alpha(IIb)beta3-initiated signaling cross-talks. J Biomed Sci 12, 841-852. (Article from our research team)
13. Chang, H. H. & Lo, S. J. (2007). Snake venom disintegrin rhodostomin served as a molecular tool to dissect the integrin function. Toxin Reviews 26, 189-202. (Review article from our research team)
最後更新日期 Oct/18/2010 新侯德珊工作室版權所有
您是龍千禧年第
位到訪的佳賓
